Configuring Dual Registration for SIP Entity
Some SIP entities (e.g., IP Phones) are setup to register with two registrar/proxy servers (primary and secondary). The reason for this is to provide call redundancy for the SIP entity in case one of the proxy servers fail. When the SIP entity registers with the proxy servers, it sends two identical REGISTER messages - one to the primary proxy and one to the secondary proxy. When the device is located between the SIP entity and the two proxy servers, it needs to differentiate between these two REGISTER messages even though they are identical. This is crucial to ensure that the device forwards the two registrations to the proxy servers and that the device performs correct call routing between the SIP entity and the two proxy servers.
To differentiate between these REGISTER messages, a unique SIP Interface needs to be used for each REGISTER message. Each REGISTER message is registered in the registration database using a unique "ac-int=<value>" string identifying the SIP Interface for the Contact user. In addition, for SIP requests (e.g., INVITE) from the proxy servers, the device needs to search its registration database for the contact user so that it can forward it to the user. In normal registration, the host part of the Request-URI contains the IP address of the device and therefore, there is no way of knowing which registered user the INVITE is intended for. To overcome this issue, you can configure the device to use a special string with a unique value, "ac-feu=<value>" for each registration, allowing the device to differentiate between two registrations from the same user (identical REGISTER requests). Each REGISTER message is registered in the registration database using the unique "ac-feu=" string identifier for the Contact user.
A summary of how the device registers the two REGISTER messages in its registration database is as follows:
|
1.
|
The addresses of the proxy servers that are configured on the SIP entity (IP Phone) must be the device's IP address with a different SIP local port for each one, for example: |
|
●
|
Primary Proxy Server: 172.17.0.1:5060 |
|
●
|
Secondary Proxy Server: 172.17.0.1:5080 |
|
2.
|
When the device receives two identical REGISTER messages from the SIP entity, it differentiates them by the SIP port on which they are received. The port allows the device to associate them with a SIP Interface (5060 for "Interface-1" and 5080 for "Interface-2"). |
|
3.
|
The device performs SIP message manipulation (Pre-classification Manipulation) on the REGISTER messages to add a special parameter ("ac-int=<value>") to the Contact header to identify the SIP Interface on which each message is received. For example: |
|
●
|
REGISTER for Primary Proxy received on SIP Interface "Interface-1": |
REGISTER
To: <sip:100@example.com>
Contact: <sip:100@172.17.100.20;ac-int=1>
|
●
|
REGISTER for Secondary Proxy received on SIP Interface "Interface-2": |
REGISTER
To: <sip:100@example.com>
Contact: <sip:100@172.17.100.20;ac-int=2>
|
4.
|
The device adds to the Contact header a special string with a unique value, "ac-feu=<value>" for each registration (e.g., "Contact: <sip:100@172.17.100.20;ac-int=1;ac-feu=x>"). |
|
5.
|
The device saves the two contacts (100@172.17.100.20;ac-int=1;ac-feu=x and 100@172.17.100.20;ac-int=2;ac-feu=y) under the same AOR (100@example.com) in its user registration database. |
The SIP call flow for dual registration is shown below:
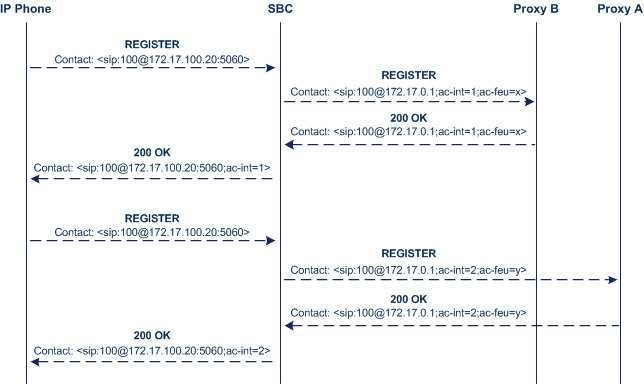
The basic SIP call flow for INVITEs to and from the registered user is shown below:
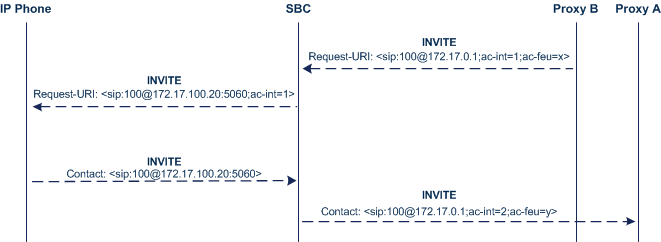
|
➢
|
To configure support for dual registration: |
|
1.
|
On the SIP entity (IP Phone), configure the primary and secondary proxy server addresses as the IP address of the device and where each address has a different SIP port number. |
|
2.
|
Open the SBC General Settings page (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > SBC folder > SBC General Settings), and then from the 'Keep Original User in Register' drop-down list, select Keep user; add unique identifier as URI parameter. |
|
3.
|
In the Message Manipulations table, configure the following rules: |
|
◆
|
Action Subject: header.contact.url.ac-int |
|
◆
|
Action Subject: header.contact.url.ac-int |
|
4.
|
In the SIP Interfaces table, configure the following SIP Interfaces: |
|
●
|
Index 0 (SIP Interface for IP Phone A): |
|
◆
|
Pre-classification Manipulation Set ID: 1 |
|
●
|
Index 1 (SIP Interface for IP Phone B): |
|
◆
|
Pre-classification Manipulation Set ID: 2 |
|
5.
|
In the Proxy Sets table, configure a Proxy Set for each proxy server (primary and secondary): |
|
◆
|
SBC IPv4 SIP Interface: Interface-1 |
|
◆
|
Proxy Address: 200.10.10.1 |
|
◆
|
SBC IPv4 SIP Interface: Interface-2 |
|
◆
|
Proxy Address: 200.10.10.2 |
|
6.
|
In the IP Groups table, configure the following IP Groups: |
|
◆
|
Classify By Proxy Set: Enable |
|
◆
|
Classify By Proxy Set: Enable |
|
7.
|
In the Classification table, configure rules to classify calls from the IP Phones based on SIP Interface: |
|
◆
|
Source SIP Interface: Interface-1 |
|
◆
|
Source IP Group: IP-Phone-A |
|
◆
|
Source SIP Interface: Interface-2 |
|
◆
|
Source IP Group: IP-Phone-B |
|
8.
|
In the IP-to-IP Routing table, configure the routing rules: |
|
◆
|
Source IP Group: IP-Phone-A |
|
◆
|
Destination IP Group: Primary-Proxy |
|
◆
|
Source IP Group: Primary-Proxy |
|
◆
|
Destination IP Group: IP-Phone-A |
|
◆
|
Source IP Group: IP-Phone-B |
|
◆
|
Destination IP Group: Sec-Proxy |
|
◆
|
Source IP Group: Sec-Proxy |
|
◆
|
Destination IP Group: IP-Phone-B |

